
A basic CNC Machining Center refers to a Computerized Numerically Controlled Milling Machine. This Machining Center will have a minimum of 3 axis, referred to as X, Y, and Z. It will incorporate a milling or drilling type tool mounted in a rotating spindle. The workpiece to be machined will be clamped or “fixtured” on the X-axis (see below) and typically does not rotate. A CNC Machining Center will also include an automatic tool changer versus a basic Milling Machine that utilizes one type of cutting tool that is manually changed.
 The rotating spindle is at the heart of every CNC Machining Center. It is mounted either in a vertical orientation, with the spindle nose / tool connection pointing downward, or in a horizontal orientation, with the spindle nose / tool connection pointing forward. The spindles are belt driven, direct coupled to a drive motor, or have an integral motor referred to as a motorized spindle. The spindle is the most critical component of the CNC Machining Center. It controls and ultimately determines the overall geometry and quality of the workpiece.
The rotating spindle is at the heart of every CNC Machining Center. It is mounted either in a vertical orientation, with the spindle nose / tool connection pointing downward, or in a horizontal orientation, with the spindle nose / tool connection pointing forward. The spindles are belt driven, direct coupled to a drive motor, or have an integral motor referred to as a motorized spindle. The spindle is the most critical component of the CNC Machining Center. It controls and ultimately determines the overall geometry and quality of the workpiece.
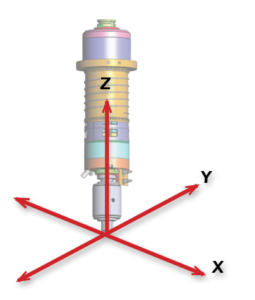
A CNC Machining Center with a vertically mounted spindle has the spindle mounted to the Z axis. The Z-axis moves up & down. The X-axis moves left to right and mounts to the Y-axis. The Y axis moves front to rear. All three axis are independent mechanical units. A precision ball screw controlled by the CNC machine moves each axis in precise increments.
Can you picture a 3-Axis CNC Machining Center?
Over time, the CNC Machining Center has evolved into a fantastic tool with vast capabilities. Many incorporate additional features with benefits that improve the machining capabilities and manufacturing value. Some of these include;
CNC machining centers are one of the most widely used machine tools in today’s manufacturing industries.
Successful CNC machining relies on the quality and reliability of machine tool parts. Any component inefficiencies have a significant effect on your overall operations. Setco sets the standards in the design, manufacture, and repair of precision CNC spindles, slides, milling heads, and other components. Our skilled and experienced technicians can guide you through your CNC machining upgrades, boosting quality and efficiency.
Contact us today to learn more about our quality CNC machining components and services.